¶ Learning Outcomes
- Explain the mode of action of enzymes in terms of an active site, enzyme-substrate complex, lowering of activation energy and enzyme specificity
- Explain enzyme action in terms of the ‘lock and key’ hypothesis
- Explain the effects of temperature and pH on the rate of enzyme catalyzed reactions
¶ Chemical Reactions in the Human Body
¶ Metabolism
-
Metabolism
- Is the sum of all the chemical reactions taking place within a living organism
- Is made up of anabolism and catabolism
-
Anabolism
- In Anabolic reactions, simple molecules combine to form complex molecules, with an input of energy (A + B + Energy → C)
- e.g. Photosynthesis
- Catabolism
- In Catabolic reactions, complex molecules break down into simple molecules, with a release of energy (C → A + B + Energy)
- e.g. Respiration
¶ Chemical Reactions
- Under normal physiological conditions, successful collisions between reactants occur very rarely
- For a successful chemical reaction to take place, reactants must
- Collide in the correct orientation
- With enough activation energy (Is the minimum energy required for a chemical reaction to occur)
¶ Explain the mode of action of enzymes in terms of an active site, enzyme-substrate complex, lowering of activation energy and enzyme specificity
¶ Enzymes
- Are proteins that function as biological catalyst
- Speed up chemical reactions by providing an alternative path of lower activation energy
- Remain uncharged at the end of reaction (thus required in small amounts)
¶ Enzymes as Catalysts
- Since enzymes remain chemically unchanged at the end of a reaction,
- They can be reused
- Only a small amount of enzymes is required to convert a large amount of substrates
¶ Enzymes as Proteins
- Due to the specific three-dimensional conformation/shape of the active site that is complementary to the substrate,
- Enzymes are substrate-specific: Each type of enzyme only interacts with one type of substrate
- Enzyme activity is affected by temperature, pH and relative substrate and enzyme concentration
- An irreversible change in the 3D structure of an enzyme is known as denaturation
- When an enzyme is denatured, there is loss or change in the active site
- The substrate can no longer fit into the enzyme’s active site and hence, no reaction can take place
¶ Explain enzyme action in terms of the ‘lock and key’ hypothesis.
¶ Lock & Key Hypothesis
- An enzyme (lock) has a specific three dimensional shape which contains an active site
- Only the substrate (key) with a three dimensional shape complementary to that of the active site can fit into the enzyme to form an enzyme-substrate complex
- The chemical reaction occurs and the substrate molecule is converted into product molecules while the substrate is attached to the enzyme
- The products then detach from the active site to bind to more substrates
- The enzyme remains unchanged at the end of the reaction.
¶ Explain the effects of temperature and pH on the rate of enzyme catalyzed reactions
¶ Temperature
- At low temperatures,
- Enzymes are less active as they have low kinetic energy
- Chances of substrate & enzymes molecules colliding are low
- Rate of reaction is low (but not zero)
- As temperature increases,
- Rate of enzyme-catalysed reaction increases (usually reaction rate doubles for every 10°C increase*)
- Increase in kinetic energy of enzyme and substrate molecules increase chance of successful collision
- At optimum temperature,
- The rate of formation of enzyme-substrate complex increases
- The rate of reaction is highest
- The optimum temperature for different enzymes varies
- Beyond the optimum temperatures,
- The enzyme activity decreases as the enzyme is denatured
- High temperature breaks the bond within the enzyme and changes its 3-D shape
- The active site of the enzyme loses its complementary shape
¶ pH
- At optimum pH,
- Rate of reaction is highest as enzymes are most active
- Optimum pH varies for different enzymes
- Away from optimum pH,
- Rate of reaction decreases as the enzyme’s active site does not fit as well to the substrate
- If enzyme is still within the pH range, it is possible for the enzyme activity to return to optimum level
- Away from optimum pH,
- Rate of reaction decreases as the enzyme’s active site does not fit as well to the substrate
- Small changes in pH may change the electrostatic charges on the surfaces of the active site and substrate, causing electrostatic repulsion between substrate and active site*
- If enzyme is still within the pH range, it is possible for the enzyme activity to return to optimum level
- At extreme pH,
- Rate of reaction is zero as the enzyme is irreversibly denatured
¶ Enzyme Concentration*
- As substrate concentration increases from relatively low levels,
- Rate of reaction increases linearly rapidly
- At there are more enzyme than substrate molecules, substrate molecules that are added will fit immediately into empty active sites of enzyme molecules
- As substrate concentration increases to relatively moderate levels,
- Rate of reaction slows down and only increases gradually
- As substrate concentration continues to increase, the number of active sites available for substrates molecules to bind to decreases
- As substrate concentration increases to relatively high levels,
- It will reach a concentration where all active sites of enzyme molecules are occupied at any time (saturation point)
- As substrate concentration increases beyond saturation point,
- Rate of reaction remains constant
- Further increase in substrate concentration will not increase rate of reaction because no active sites are immediately available (Enzyme is limiting the rate of reaction)
- Further increase in rate of reaction can be done by increasing enzyme concentration, temperature or adjusting closer to optimum pH
¶ Substrate Concentration*
- When enzyme concentration < substrate concentration,
- Rate of reaction increases linearly rapidly then gradually
- Newly added active sites are available to bind substrates
- When enzyme concentration = substrate concentration,
- Saturation point is reached
- When enzyme concentration > substrate concentration,
- Rate of reaction remains constant
- Newly added active sites have no substrates to bind to
- Substrate becomes limiting
¶ Limiting Factor*
- A limiting factor is a factor that affects the rate of reaction if its quantity is changed
- Increasing the value of this factor will increase the rate of reaction
- Increasing the value of other factors will not increase the rate of reaction
¶ Inhibitors*
- An inhibitor is a molecule that binds to an enzyme and decreases its activity
- A competitive inhibitor binds to the active site and prevents the substrate from binding
- A non-competitive inhibitor binds to another site (allosteric site) on the enzyme which changes the shape of the active site
¶ Importance of enzymes
¶ Catalyze Metabolic Reactions in the Body
- Without enzymes, metabolic processes will not proceed at a rate fast enough to sustain life
- Some conditions linked to enzyme deficiency are:
- Lactose Intolerance
- Lack of enzyme (lactase) to break down milk sugar (lactose) resulting in indigestion (abdominal pain, bloating, flatulence, nausea, and diarrhoea)
- G6PD
- Medical condition where the body lacks the enzyme, glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase, which is important for maintaining the red blood cell
- *Galactosemia
- Different enzymes involved in breaking down galactose are affected, which leads to jaundice, vomiting and liver enlargement after breast or formula feeding of newborn
- Lactose Intolerance
¶ Industrial Uses
- Enzymes
- Speed up many industrial process
- Their specificity ensures only a specific process is targeted without affecting the other processes
- They may reduce cost as they are only required in small amounts
- They reduce environmental pollution as they are biodegradable as compared to some other chemicals
- In the food industry
- The enzyme invertase is used to make chocolates with soft centres (e.g. After eight and Kinder bueno)
- A mixture of sucrose and glucose syrup that has high proportion of sucrose is added with invertase before being molded and coated with melted chocolate
- Invertase (enzyme from yeast) slowly converts sucrose to more soluble and sweeter sugars (glucose and fructose), which gives it a creamy texture


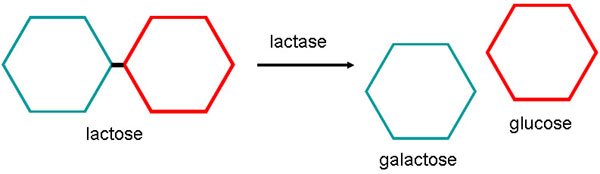
- Enzymes are used to make lactose-free products
- The enzyme lactase is used to create lactose-free products as some people are lactose-intolerant
- Lactase is extracted from a fungi (e.g. Aspergillus oryzae)
- Lactase will break down lactose into glucose and galactose

- Enzymes are used to make clear fruit juices
- Pectinases are used in the preparation of fruit juices and vegetable juices in order to increase the juice yield
- Particularly in the case of berries, pectinases improve the extraction of colourings and aromas
- In some cases, they clarify naturally cloudy juices
- Pektinases primarily are obtained through fermentation with fungal cultures
- Enzymes are used to make wine
- To make wine to have a stronger aroma or enhancing the aroma, glucosidase is used
- Glucosidase breaks down the glucosides which contains the non-free volatile aroma and sugar
- The enzyme invertase is used to make chocolates with soft centres (e.g. After eight and Kinder bueno)
- In the cleaning industry
- Detergent contains enzymes to remove stains from clothes
- Works best at low temperatures (<50°C) as enzymes are proteins which denature at high temperatures
- In the textile industry
- Enzymes are used in the treatment of fabrics
- Desizing
- Fabrics are often covered by starch (or its deritvatives) prevent the threads breaking during weaving through a process known as sizing
- After weaving, the starch must be removed before it can undergo other processes (bleaching, dyeing, printing etc.)
- This process (desizing) is carried out by starch-splitting enzymes (alpha-amylases)
- As amylases are specific and efficient in small amounts, it removes the size without any harmful effects on the fabric and reduces cost
- Bio-stoning (Fading of denim in jeans)
- Denim finishers make use of the enzyme cellulase to accelerate abrasion that fades the denim by loosening the indigo dye on the denim
- Bio-polishing
- A finishing process to soften fabrics and reduce fuzziness and pilling of the cellulosic fibre
- Enzyme cellulases hydrolyze the micro fibrils (hairs or fuzz or pills) protruding from the surface of yarn which then break off to leave a smoother and softer fabric surface
- In the biomedical industry
- Enzymes are used to test for medical conditions
- Enzymes are used in the urine glucose test
- Measures the amount of sugar in a urine sample
- Glucose is usually not found in urine
- Levels of glucose beyond 0.8 mmol/L may indicate diabetes, pregnancy or other diseases
- Tip of the paper strip contains two enzymes, glucose oxidase and peroxidase
- Glucose oxidase converts glucose to hydrogen peroxide
- Hydrogen peroxide reacts with a colour-changing chemical in presence of peroxidase
- The intensity of colour indicates glucose concentrationt
- *Enzymes are used in the pregnancy kit test